Definition
Bollinger Bands consist of a middle band, which is a moving average of a security's price, and two outer bands that are calculated based on standard deviations from this moving average. When the bands expand, it suggests an increase in market volatility, and when they contract, it indicates decreased volatility. The price of a security typically fluctuates within these bands.
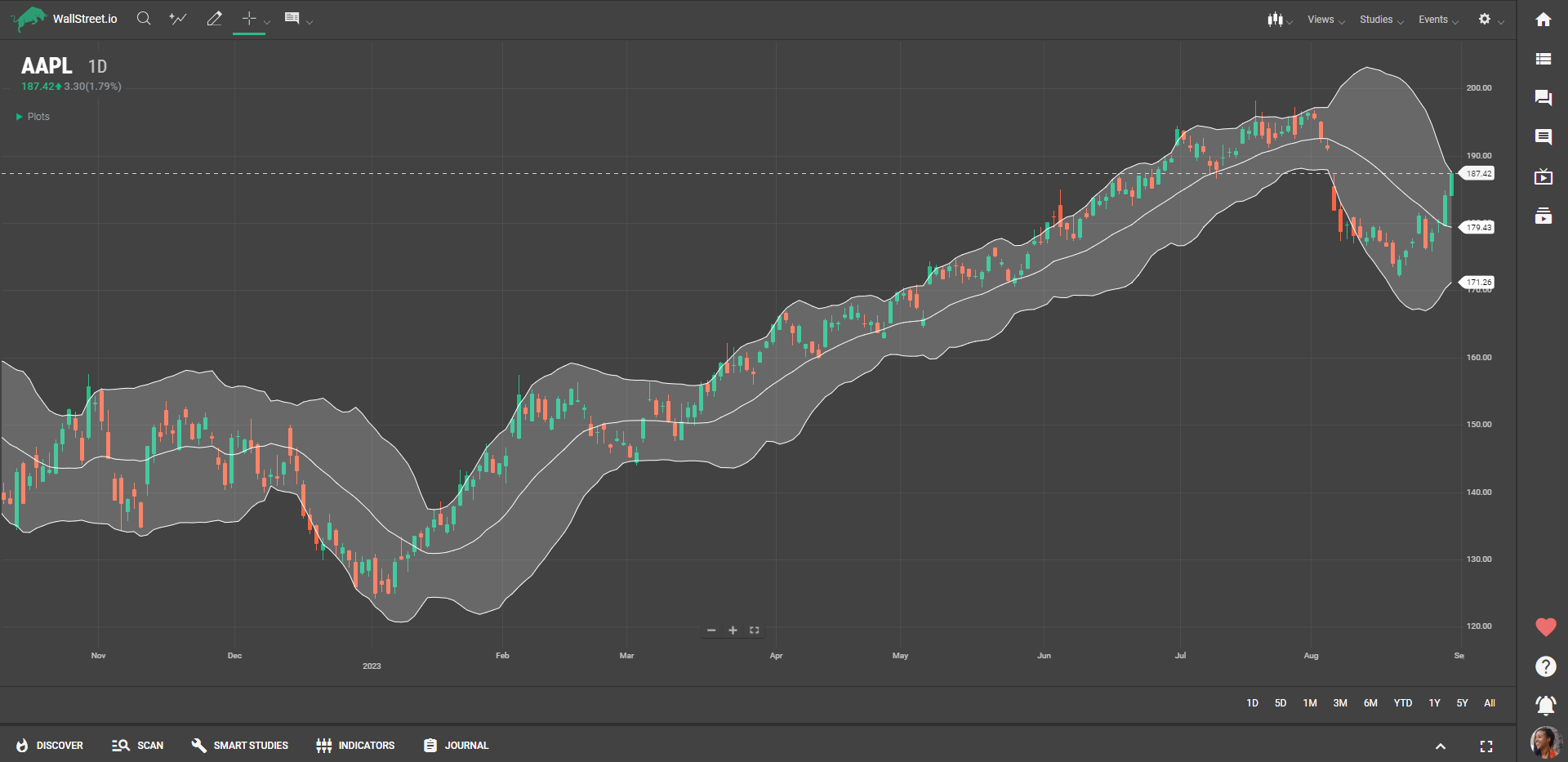
Suggested Trading Use
Bollinger Bands are versatile and can be used in various ways for trading:
Spotting Overbought/Oversold Conditions: If the price is touching or moving outside the upper band, it could mean the stock is overbought. Conversely, if it's near or outside the lower band, the stock may be oversold.Identifying Breakouts: A price that moves outside of the Bollinger Bands can signal a significant price movement. Traders often use these potential breakouts as trading opportunities.Volatility Indication: The width of the bands can also be used to gauge market volatility. Widening bands suggest increasing volatility, while narrowing bands indicate decreasing volatility.Trend Following: In a strong uptrend, prices usually hover around the upper band, while in a downtrend, they tend to stay close to the lower band.Squeeze Patterns: When the bands come close together ("squeeze"), it can often be the precursor to a significant price move. A squeeze suggests that a breakout is imminent.



 Discover Tab Reference Guide
Discover Tab Reference Guide Discover Tab How-To Guide
Discover Tab How-To Guide Smart Studies How-To Guide
Smart Studies How-To Guide Smart Studies Reference Guide
Smart Studies Reference Guide Scan Tab Reference Guide
Scan Tab Reference Guide Scan Tab How-To Guide
Scan Tab How-To Guide Watchlists How-To guide
Watchlists How-To guide Watchlists Reference Guide
Watchlists Reference Guide Chatrooms Reference Guide
Chatrooms Reference Guide Community Wall How-To Guide
Community Wall How-To Guide Community Wall Reference Guide
Community Wall Reference Guide Streams Reference Guide
Streams Reference Guide Streams How-To Guide
Streams How-To Guide