Filter List panel
Whether you're a seasoned trader or just starting out, our platform makes strategy discovery as straightforward and personalized as it can get. Our Filter Tool empowers you to refine your search by applying various criteria, so you find strategies that truly match your trading style and goals.
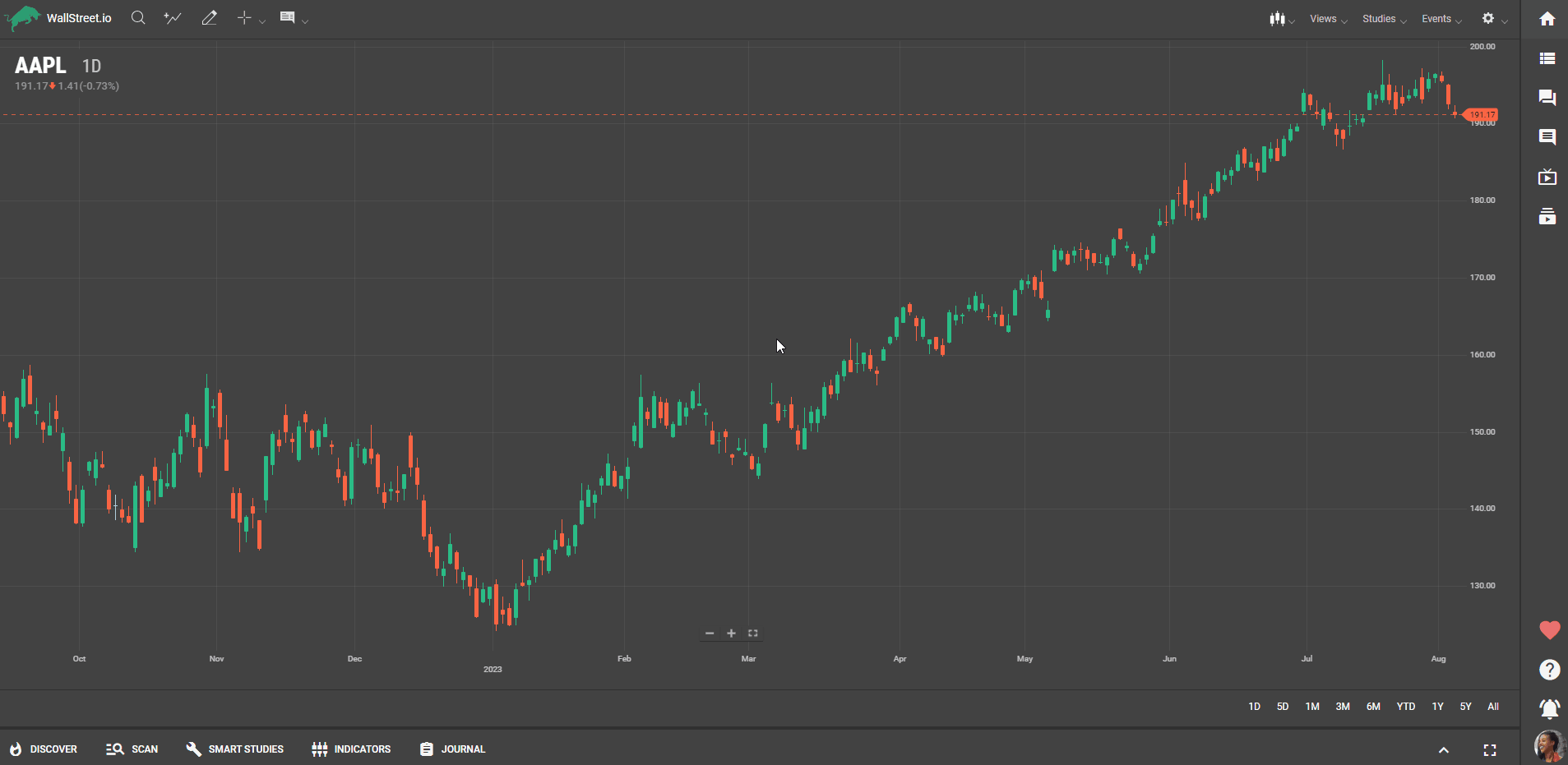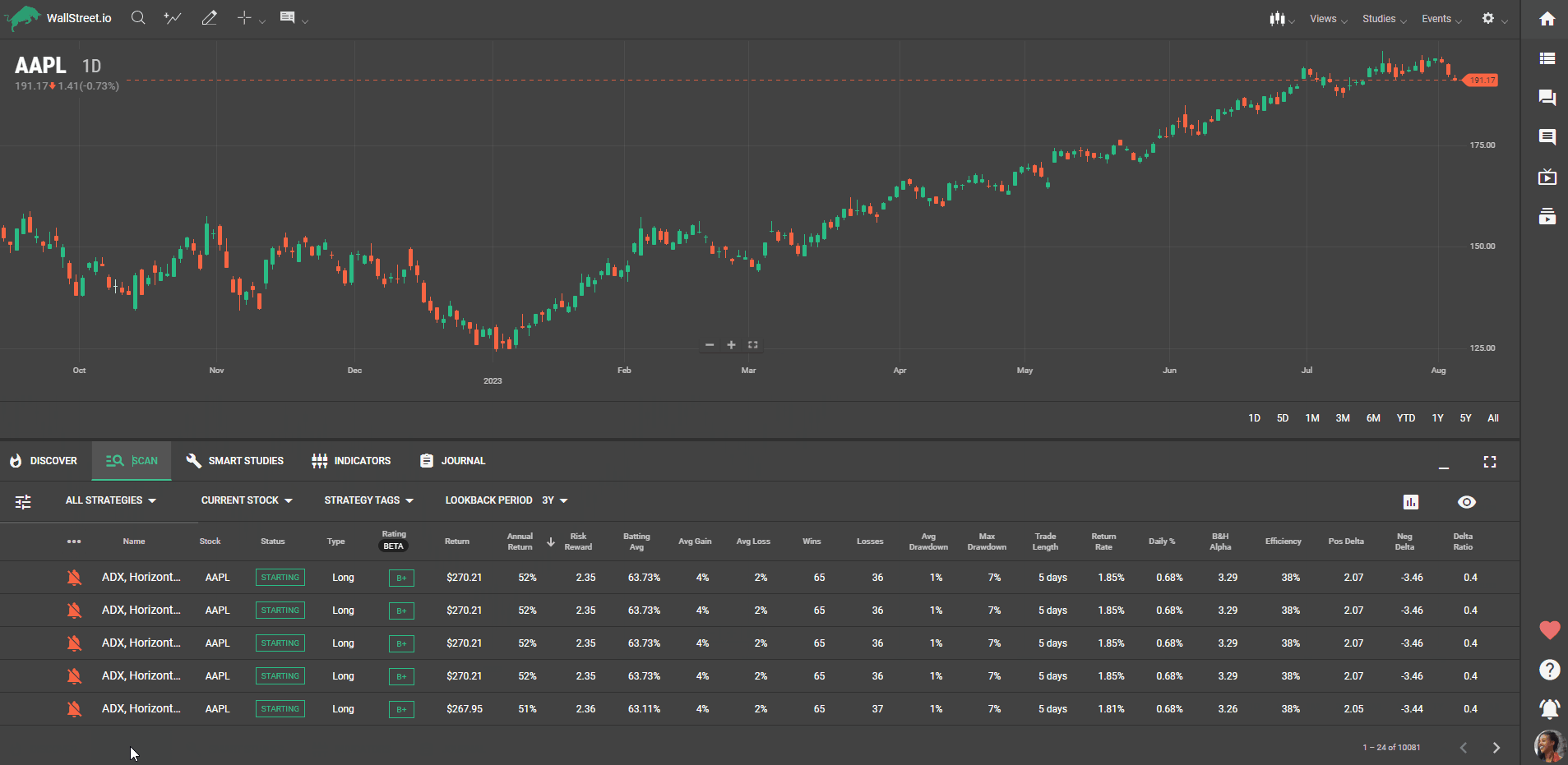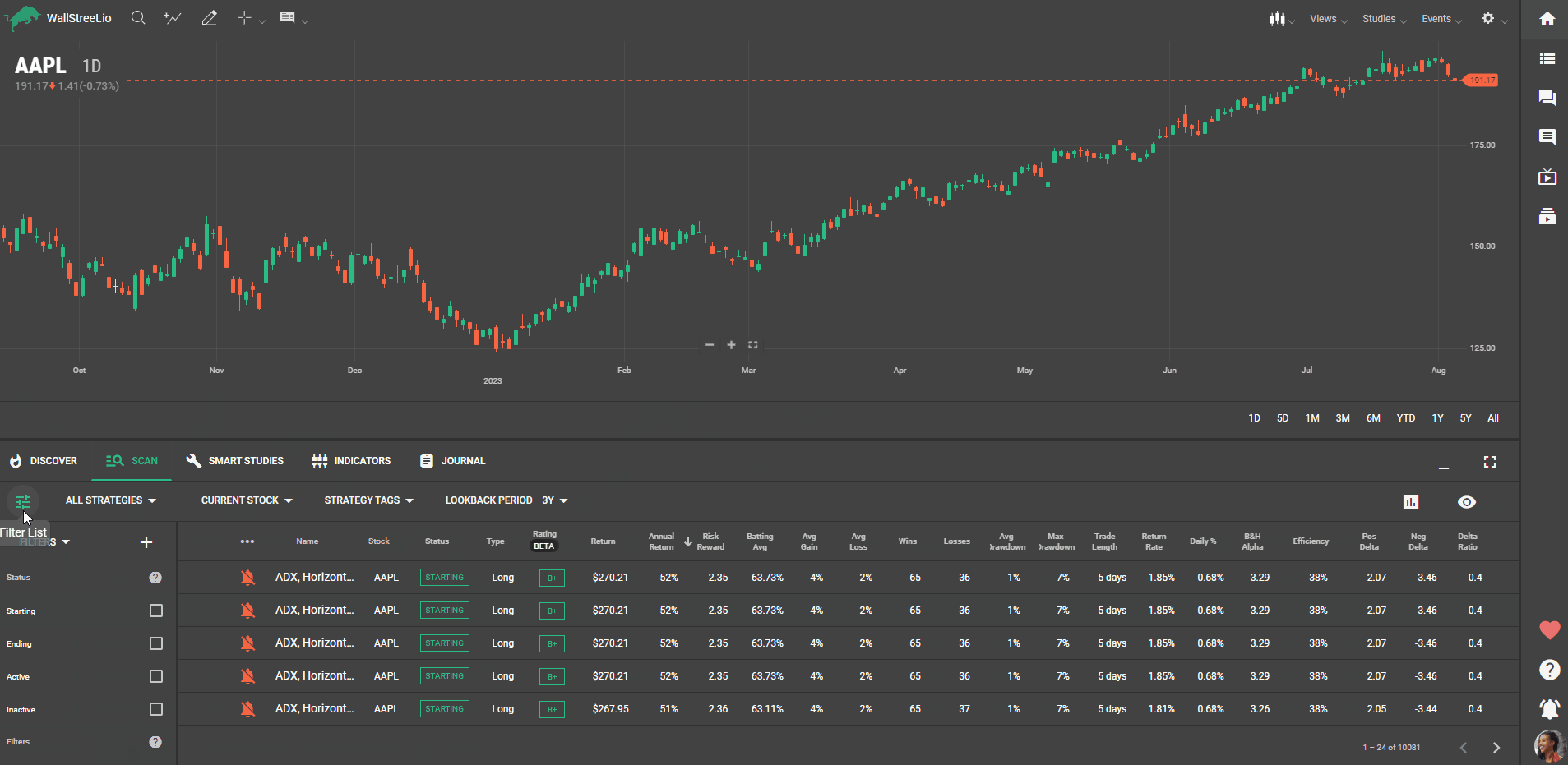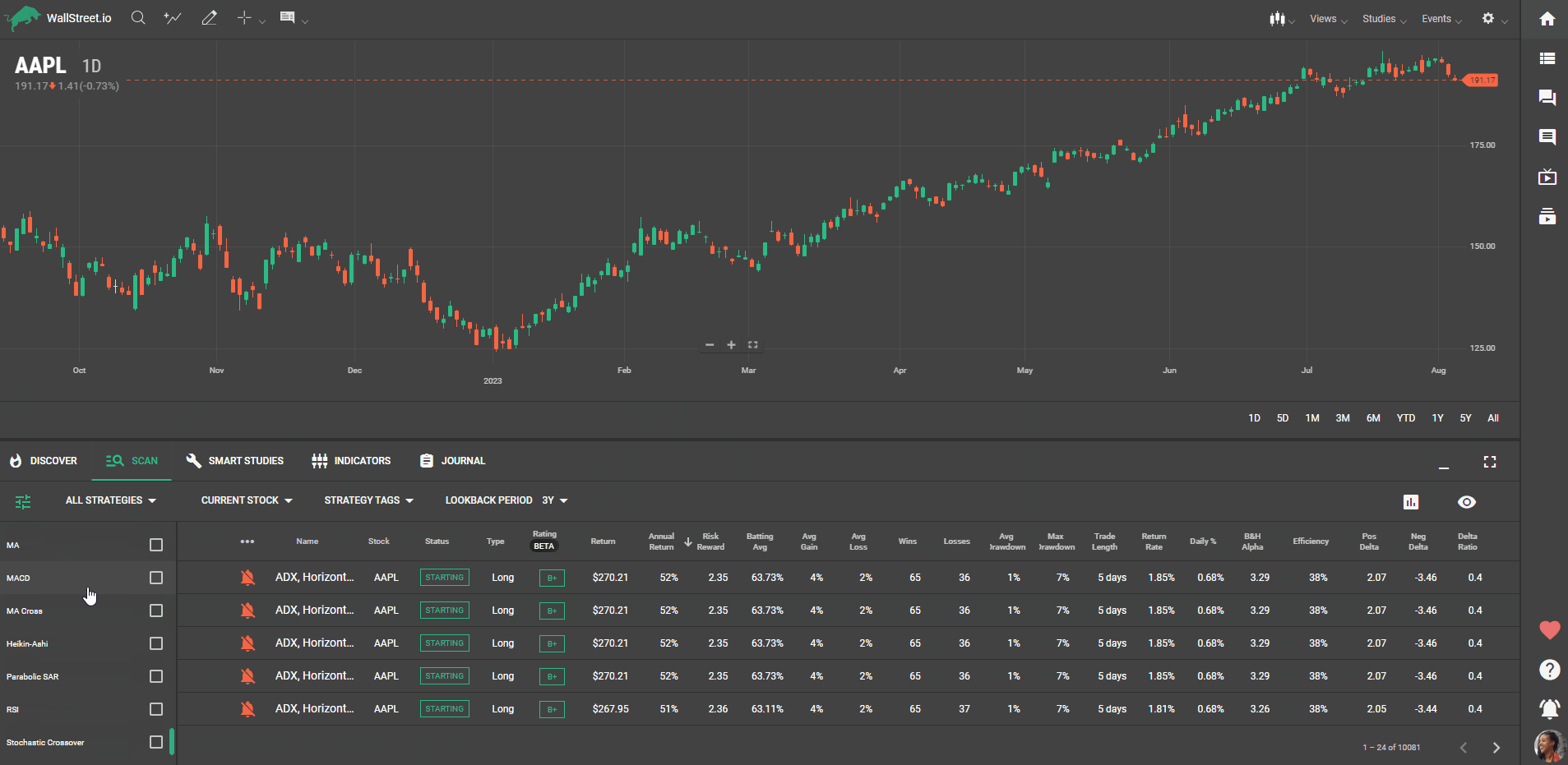
Each strategy on our platform has specific characteristics, and understanding them is vital to finding the perfect fit. This guide will walk you through what each status and statistic filter mean, how to use them, and why they matter to your strategy search.
Status
Starting: This means that the conditions that make up the strategy are true as of today. True means they are happening.Ending: This means that the conditions that make up the strategy are no longer true as of today.Active: This is when the conditions for the strategy are true and have been true for more than one day.Inactive: This means that the conditions that make up the strategy are not true today.Statistic Filters
Stock Price: Allows you to filter strategies based on the stock price of the underlying instrument. You can set specific price ranges to narrow down your search.Rating: Provides a measure of the rating assigned to trading strategies. The rating can indicate the performance or quality of a strategy, often based on historical backtesting or user feedback.Annual Return: Filters strategies based on their annualized return, which represents the average percentage return per year over a specific period. You can set minimum or maximum thresholds to find strategies that meet your desired return criteria.Risk-Reward Ratio: Enables you to filter strategies based on their risk-reward ratio, which compares the potential gain of a trade to the potential loss. A higher ratio indicates a potentially more favorable risk-reward profile.Batting Average: Filters strategies based on their batting average, which represents the percentage of winning trades out of the total number of trades. It provides an indication of a strategy's consistency in generating profitable trades.Average Gain: Allows you to filter strategies based on the average percentage gain per trade. It provides insights into the average profit potential of the strategy.Average Loss: Filters strategies based on the average percentage loss per trade. It helps you assess the potential downside risk associated with the strategy.Wins: Enables you to filter strategies based on the total number of winning trades. It provides an indication of the strategy's success rate in generating profitable trades.Losses: Filters strategies based on the total number of losing trades. It helps you understand the frequency of losing trades associated with the strategy.Average Drawdown: Allows you to filter strategies based on the average drawdown, which measures the peak-to-trough decline during a specific period. It indicates the maximum potential loss a strategy may experience.Max Drawdown: Filters strategies based on their maximum drawdown, representing the largest peak-to-trough decline observed over a specific period. It helps you assess the worst-case scenario for potential losses.Trade Length: This enables you to filter strategies based on the average duration of trades. It provides insights into the holding period of positions associated with the strategy.Trades per Year: Filters strategies based on the average number of trades executed per year. It helps you understand the trading frequency of the strategy.Average Return: Allows you to filter strategies based on the average percentage return per trade. It provides insights into the profitability of individual trades associated with the strategy.Daily Gain: Filters strategies based on the average daily gain, representing the average percentage increase in value per day. It helps you assess the potential daily profitability of the strategy.Buy and Hold Alpha: This enables you to filter strategies based on the buy and hold alpha, which measures the excess return generated by the strategy compared to a simple buy and hold approach.Efficiency: Filters strategies based on their efficiency, which represents the ratio of the strategy's average gain to its average loss. A higher efficiency ratio indicates a potentially more efficient use of capital.Positive Delta: Allows you to filter strategies based on their positive delta, which represents the difference between the strategy's average gain and average loss.Negative Delta: Filters strategies based on their negative delta, which represents the negative difference between the strategy's average gain and average loss.Delta Ratio: This enables you to filter strategies based on their delta ratio, which is calculated as the positive delta divided by the negative delta. It provides insights into the risk-reward relationship of the strategy.Strategy Type
Long: When a trader takes a long (or “bullish”) position, it means they are buying an asset with the expectation that its price will rise over time. In other words, they believe the value of the asset will appreciate. By going long, traders aim to profit from an increase in the asset's price. To establish a long position, a trader typically buys the asset and holds it in their portfolio until they decide to sell it at a higher price.Short: When a trader takes a short (or “bearish”) position, it means they are selling an asset that they do not own with the anticipation that its price will decline. Essentially, they are betting on a decrease in the asset's value. To establish a short position, traders typically borrow the asset from a broker and sell it on the market. Later, they repurchase the asset at a lower price to return it to the broker, profiting from the price difference.Studies Conditions
ADXBollinger BandsKeltner ChannelDMIMAMACDMA CrossHeikin-AshiParabolic SARRSIStochastic CrossoverStochastic ThresholdWilliams %RFor a deep-dive on how to best use these Studies Conditions, review our Smart Studies Reference Guide.



 Discover Tab Reference Guide
Discover Tab Reference Guide Discover Tab How-To Guide
Discover Tab How-To Guide Smart Studies How-To Guide
Smart Studies How-To Guide Smart Studies Reference Guide
Smart Studies Reference Guide Scan Tab Reference Guide
Scan Tab Reference Guide Scan Tab How-To Guide
Scan Tab How-To Guide Watchlists How-To guide
Watchlists How-To guide Watchlists Reference Guide
Watchlists Reference Guide Chatrooms Reference Guide
Chatrooms Reference Guide Community Wall How-To Guide
Community Wall How-To Guide Community Wall Reference Guide
Community Wall Reference Guide Streams Reference Guide
Streams Reference Guide Streams How-To Guide
Streams How-To Guide